OptimiX XFR - Forecast & Replenishment
APS supply chain solution that optimizes your inventories and helps you fine-tune your forecasts.
Align your inventory with actual demand thanks to AI-generated forecasts. Our optimization engine helps you improve your service rate and reduce stock-outs by up to 75% !
Supply chain - APS
OptimiX Forecast & Replenishment
Efficiently plan and manage your supplies with an AI-based forecasting engine.
Values
Stock
Forecast accuracy
Without
52.7M€
79.0%
With
46.7M€
95%
Sales 2024
153,4M
10.43%
XFR - A data-driven procurement solution that aligns your inventory with reality on the ground.
Forecasts that are too far removed from reality disrupt your planning, generate overstocks or shortages, and impact your operational performance. Add to this the difficulty of anticipating fluctuations in demand or logistical hazards.
Optimix Solutions’ APS XFR solution enables you to accurately model your historical dataand simulate different demand scenarios and automatically orchestrate your replenishments.
The result : an agile supply chain, up to -75% stock shortages, an optimized service rate, and more reliable decisions thanks to continually recalibrated forecast data.

Why is an APS supply chain solution essential for optimizing your inventories?
Reduce out-of-stock situations by up to 75%.
Optimix XFR accurately anticipates demand and synchronizes your supplies with real market needs. You limit shelf shortages and significantly improve product availability.
95% accuracy in demand forecasts
Our AI-based forecasting engine learns from your historical data and adapts to cyclical variations to generate reliable plans. Your decisions are driven by reliable, continuously updated data.
95% product availability guaranteed
By automatically integrating your logistical constraints and supply capacities, the solution enables you to achieve a high level of service without oversizing your inventory.
+50% productivity with a collaborative platform
Centralize the management of your forecasts and supplies, automate adjustments and facilitate collaboration between supply, sales and finance teams. Concrete, measurable efficiency gains.
Those extras that make all the difference!
Reliable forecasts, concrete results
AI aligns your forecasts with reality on the ground to reduce disruptions by up to 75% and sustainably improve your operational performance.
A unified APS platform
Supply, forecasting, planning: all your supply levers integrated into a single, coherent interface for frictionless management.
Integrated financial optimization
Reduced overstocking, improved rotation and better flow management = less tied-up capital and more available cash.
Intelligent supplier tracking
Visualize supplier service levels, manage your commitments and adjust your purchasing conditions thanks to reliable, real-time indicators.
Custom business modeling
Every flow, every rule, every constraint can be configured to suit your processes. You remain in control of your organization and your priorities.
Data security and sovereignty
Secure hosting, RGPD compliance and total control over your data: your supply chain, protected and controlled from end to end.
An advanced APS Software with dashboards to anticipate and manage your procurement and sales forecasts.
Visualize your forecasts, stock levels, service rates and supplier performance in real time.
Optimix XFR solution gives you access to highly accurate demand forecasts, while monitoring your key indicators: out-of-stocks, overstocks, product availability, stock rotation.
Thanks to customizable, dynamic dashboards, you can detect points of tension, simulate different supply scenarios and adjust your decisions as closely as possible to operational realities.
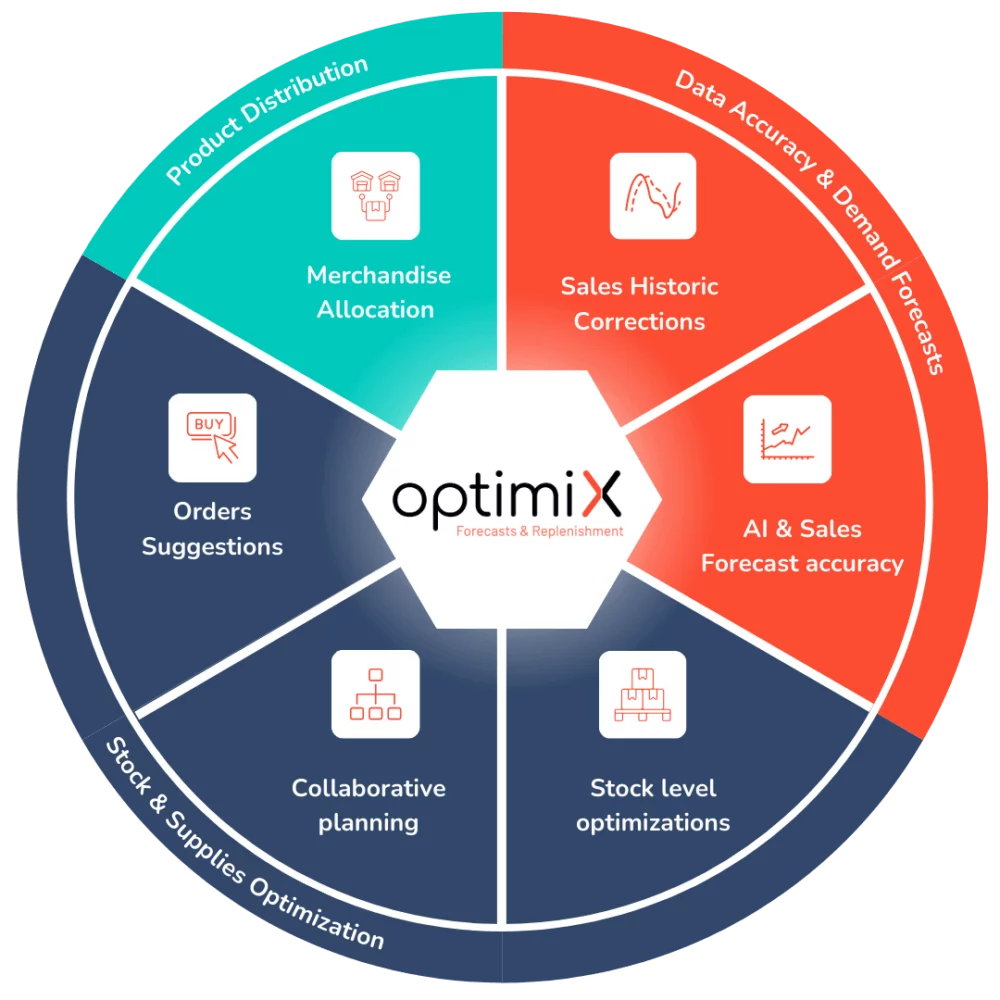
An end-to-end process to transform your supply chain data into profitable decisions
At OptimiX Solutions, our approach is based on a rigorous sequence of steps, entirely designed to meet the challenges of the supply chain.
Data collection and integration
Optimix XFR centralizes your sales data, inventory, historical data, promotions, external events and supplier data. This comprehensive database feeds forecasts and ensures consistency between your systems (ERP, WMS, POS, etc.).
Data cleansing, structuring and reliability
Your raw data is cleaned, cross-referenced and enriched for direct use. Better data means better forecasts – and better decisions.
Advanced AI modeling
Our algorithms learn from your past data, identify trends and anticipate fluctuations in demand. They take into account seasonality, disruptions, hazards and product life cycles to make your decisions more reliable.
Sourcing recommendations
The solution automatically generates optimized replenishment proposals and order projections, based on your service objectives, logistics constraints and supplier performance. You move from reactive to predictive management.
Real-time performance visualization
Take advantage of dynamic dashboards to track your key indicators: availability rate, stock coverage, service rate, out-of-stock levels, supplier reliability, etc. You can steer your business continuously, with a clear, actionable vision.
Partners who testify to our expertise and commitment.
“The tool perfectly meets our users’ expectations, thanks to total transparency in its operation and settings.
Its management by exception and “typical week” approach have enabled us to optimize our forecasting and procurement efficiently. What’s more, integration into a standard ensures the stability and ongoing evolution of the solution, while respecting project deadlines and costs.”
Eric Gilbert
Purchasing Manager, Buffalo Grill
“Optimix is a high-performance, feature-rich solution that has improved our daily lives. Implementation was very quick, smooth and efficient.
Price management is now more efficient. We are continuing to develop the solution with functionalities adapted to our needs.
It’s essential for us to be able to keep pace with business requirements. I’m very satisfied with the collaboration, both during the deployment and today.”
Katarzyna Pieńkowska-Pawlik
Pricing Manager at Auchan Poland
“My experience in using the Optimix solution and working with the teams has been very positive.
This software has significantly improved our pricing decisions thanks to accurate information. We have benefited from a strong relationship with the OptimiX Solutions teams, and the rapid deployment in 6 months has reinforced our confidence in this successful collaboration.”
Mathieu Louchez
Pricing and Assortment Leader at Boulanger
“Thanks to optimiX Solutions’ solution, we have not only reduced the number of errors, but also maximized our analysis capabilities, in particular for segmenting our competitors (BtoB, BtoC, etc.).
Our business teams managed to halve their alignment time, with increased productivity: over 12,000 products linked in just 3 minutes.
The solution is complete and covers our needs 360 degrees. The tool is ergonomic and price management is simplified.”
Jérémi Dusong
Pricing Project Manager at Bureau Vallée
Modules designed to manage your entire supply chain from A to Z
All your supply chain needs in one integrated APS solution
Inventory and procurement optimization
Automate replenishment, taking into account your logistics constraints, service objectives and stock levels. Reduce overstocks and out-of-stocks, and improve stock rotation.
Delivery flow management
Optimize your delivery flows by anticipating receiving capacities and coordinating shipments. Reduce costs and ensure reliable, on-time deliveries.
Orders projection
Accurately project your net supplier order requirements. Visualize the impact of purchasing decisions on your future inventories, and secure your relationship with suppliers.
Why choose us?
Robustness, ease of use and adaptability are the pillars on which our solutions have been developed.
Reliable, high-performance, secure software
15 years of experience
Intuitive interface and easy handling
Expert, senior consultants
Single point of contact
100% in-house expertise: No dispersal of confidential data

THESE PLUS
THAT MAKE ALL THE DIFFERENCE
Reduced stock-outs → Increased salesFewer products missing from shelves or online, so more sales.
Reduced inventory→ Improved cash flowLess tied-up capital and better inventory turnover.
Improved product availability → Better customer satisfaction The right products, in the right place, at the right time, for a seamless customer experience.
Do you have any questions?
Who is Optimix Forecast & Replenishment designed for?
XFR is designed for retailers and multi-channel distributors who want to make their sales forecasts more reliable, automate their replenishments and optimize their inventories, whatever their volumes or the complexity of their logistics network.
What concrete benefits can I expect from XFR?
With XFR, you can achieve up to 30% reduction in operating costs, reduce analysis time by 25 to 40 and cut IT costs by 20 to 30%. integration and maintenance. You will also improve product availability while reducing overstocking.
How does demand forecasting work?
Our forecasting engine, based on advanced advanced AI algorithms integrates your sales histories, trends, calendar and promotional effects to produce reliable forecasts, even for slow-moving or irregular-cycle SKUs.
Is it possible to correct historical anomalies?
Yes, XFR identifies and automatically corrects for breaks, abnormal peaks or bias in your data. This makes forecasts more robust, even in the event of seasonality or exceptional events.
How are replenishments managed?
The solution automatically proposes optimized supply plans, taking into account your constraints (delivery frequency, MOQ, safety stock, logistics capacities, etc.). You can also simulate and adjust your order proposals according to your objectives.
Does the solution take product segmentation into account?
Yes, XFR allows fine segmentation of your products according to their behavior (ABC, XYZ, seasonality, rotation…), in order to apply differentiated and relevant forecasting and replenishment strategies.
Can I monitor my performance from a dashboard?
Absolutely. You have customizable, interactive dashboards to monitor your forecasting KPIs, availability rate, stock coverage, service rate, and quickly detect points of attention.
Is the tool collaborative?
Yes, XFR enables collaborative management between your supply, purchasing and store teams, facilitating coordination, validation of proposals and sharing of scenarios. As a result, you gain in responsiveness and alignment.
How do you integrate with our existing tools?
XFR is interoperable with most ERP, WMS and business tools on the market. Integration is rapid, with an open technical base and standard connectors, while guaranteeing a reduction in long-term maintenance costs.
What support is planned?
We start with a functional scoping phase to understand your specific business requirements and configure the solution to meet your needs. Then, you benefit from expert supportwith customized training, dedicated support and regular optimization workshops to maximize your supply chain performance.
