Developing a pricing strategy in the consumer products and services industry is relatively straightforward. Generally, the price set for a product or service is the same for all consumers, although targeted promotions may occasionally offer variations.
This price is influenced by various factors, including the company’s commercial policy and seasonal variations, while being regulated by the dynamics of supply and demand at the time of purchase.
In contrast, pricing strategy in business-to-business (B2B) commerce is significantly more complex and subject to specific constraints. This complexity is due to the very nature of B2B transactions, which often involve personalized negotiations, long-term contracts and volume considerations.
In this article, we explore the subject related to price optimization in B2B:
- complex pricing strategies,
- “price waterfall” analysis, and
- the evolution towards a data and ERP-driven approach.
Control discounts, contracts, and maximize your profitability.
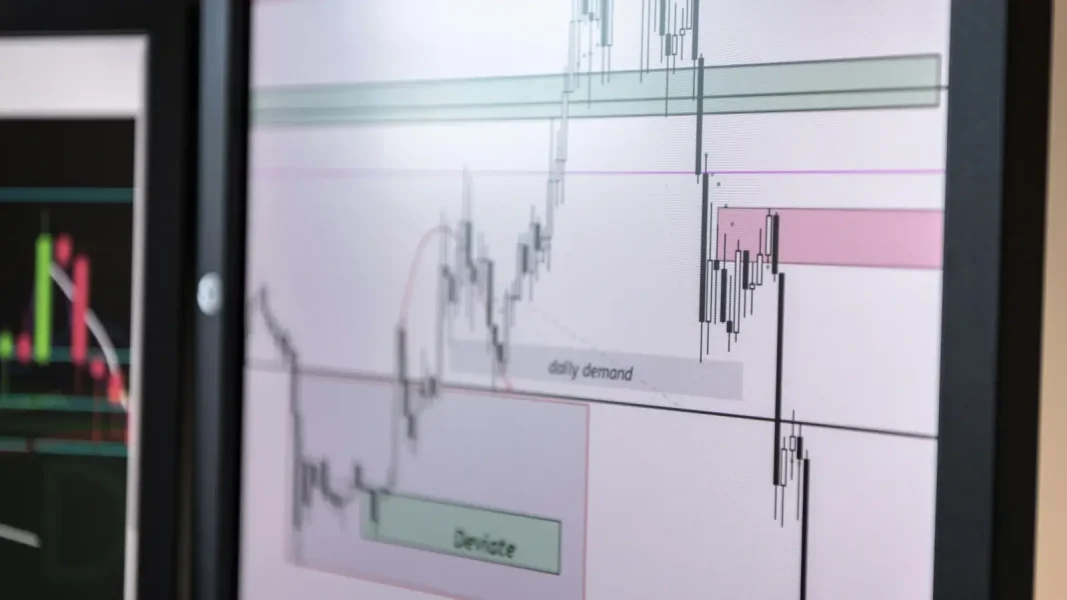
The concept of “Price Waterfall” for price optimization
In order to fully understand the subject, it is essential to define the concept of “price waterfall”.). This method of analysis makes it possible to break down the final price paid by the customer and to identify the different components that constitute it. This decomposition helps identify value maximization opportunities and potential margin shrinkage risks.
The price of a B2B product is generally made up of several elements. The first is the list price, which serves as a starting point for discussions. However, this price is rarely the final amount paid by the customer. Several types of discounts modify this base price:
- Standard discounts : these are discounts applied uniformly to all customers or to specific categories of customers. They can be based on criteria such as purchase volume or customer loyalty.
- Specific discounts : these discounts are negotiated individually with each customer. They may depend on many factors, such as order size, long-term relationship with the customer or specific customer needs.
- Spot discounts : These discounts are occasional and often used in specific situations, such as to sell excess stock or to enter a new market. They are generally short-lived and can vary considerably.
Pricing strategy in the B2B sector is a complex process that requires a thorough understanding of the different elements that influence the final price.
The Price Waterfall method is a valuable tool for breaking down these elements and optimizing the pricing strategy. By taking these different aspects into account, companies can develop more effective strategies tailored to their business objectives and the specific needs of their customers.
Evolution of price optimization in B2B
Moving from a traditional approach in the 1980s to a modern, sophisticated, data-driven method from the 2010s , this transition marks a fundamental shift in the way companies determine the price of their products and services. This has profoundly influenced their business operations and ultimately their market positioning.
From empiricism to the era of data and ERP
Initially, price optimization in B2B was based on an empirical method which was based on a fixed margin which was added to the purchasing or production costs.
It included in-depth knowledge of the sector, taking into account the specificities of the market, competition, as well as the personal relationships established by salespeople and account managers. The latter, thanks to their knowledge of customers and their sensitivity to price changes, played a key role in defining prices.
With the advent of technologies and the democratization of ERP, a shift has begun.
ERPs have indeed made it easier to access and manage data, allowing for more precise price monitoring. This evolution led to the implementation of price control mechanisms, where the sales teams’ pricing proposals were subject to validation processes, including floor prices.
Automation and rules-based approach
The next step in this transformation was the automation of pricing . This new rules-based method uses decision trees (workflow) to evaluate various factors such as:
- the category of the customer,
- the frequency and volume of orders, as well as
- payment terms.
These criteria, combined with specific KPIs, such as maximizing business volume within a specific margin, or maximizing margin for a minimum volume), lead to a data-driven price that is more transparent and easy to understand. .
This streamlined approach offers several advantages, including the harmonization of practices within sales teams.
However, it creates other challenges to overcome, for example, the adoption of this new method may lead to a restructuring of salespeople’s remuneration models and therefore modify their room for maneuver in negotiations…
The era of Big Data and predictive technologies
The ultimate step in the maturity of an organization’s pricing strategy is the adoption of predictive technologies and the exploitation of Big Data.
Use of advanced algorithms allows you to analyze a large volume of data to determine the optimal price point. This data can include strategic business information, customer-specific data, as well as contextual data. The objective is to maximize revenue while taking into account various aspects of the price waterfall.
The challenges of data-driven pricing
To succeed in this transition to data-driven pricing, it is essential that companies have quality access to their data. s. This involves not only having complete and structured information in their ERP, but also ensure that the data produced is reliable and regularly updated. It is therefore crucial to have complete and well-organized customer data in a CRM tool (GRC in French – Customer Relationship Management).
Innovation in price optimization in B2B
The evolution of B2B commerce is marked by the emergence of new pricing and distribution models, particularly with the growing adoption of e-commerce.
This transformation takes place in a context where price setting is increasingly influenced by data analysis. Many B2B manufacturers and distributors are turning to e-commerce, either by developing their own online sales sites or by using marketplaces specialized in B2B (CdiscountPRO, Mercateo etc…).
However, adapting the e-commerce platform model to B2B is not without challenges. Business relationships have specific requirements that must be taken into account. For instance, prices must be dynamic and personalized for each product family and each customer. This requires a secure and personalized environment.
In addition, platforms must be able to manage discounts and wholesale prices , as well as reflecting the complex purchasing processes typical of some organizations. Payment options should also be flexible, with varying due dates to adapt to the needs of B2B customers.
These specificities inherent to the B2B sector are directly linked to the pricing strategy . Businesses should consider them carefully before embarking on online sales. Success in this area requires a deep understanding of customer needs and behaviors, as well as as an ability to integrate advanced technologies to provide a personalized and efficient user experience.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
The adoption of e-commerce by B2B companies marks a major transformation in their sales and distribution approaches. By implementing pricing strategies and innovative distribution and by optimizing their prices, these companies are not just improving their operational efficiency; they also enrich the customer experience, a key factor in maintaining their competitiveness in a constantly evolving market.
Using pricing optimization and management software, such as Optimix XPA, offers B2B brands the possibility of setting competitive prices for their products and services. This technology is proving particularly valuable to businesses with tight margins, providing them with essential support in managing their finances.
To find out how an optimal B2B pricing strategy can strengthen your sales cycle and drive growth, don’t hesitate to chat with our pricing experts or request a demo.